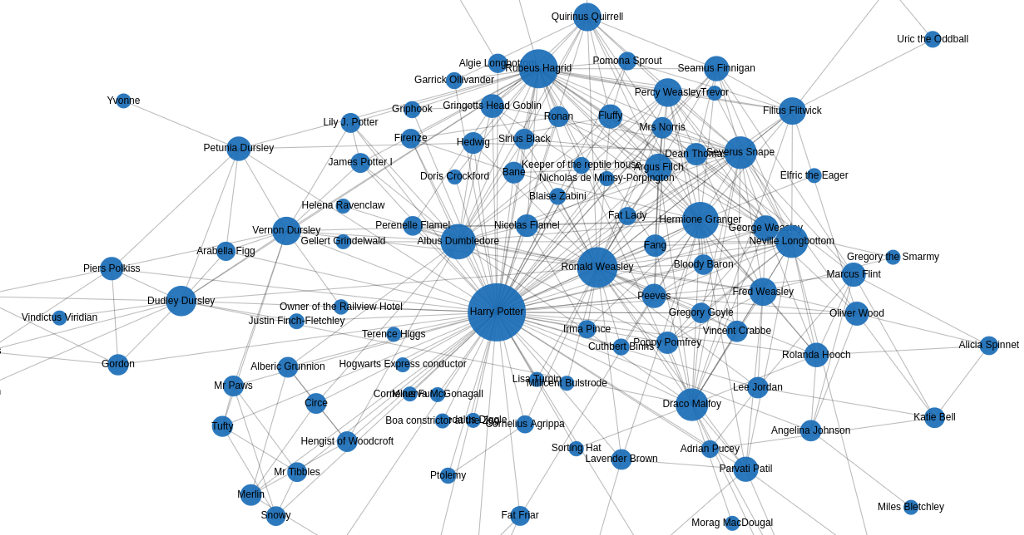
The Google Knowledge Graph is a semantic search database and technology developed by Google to enhance search results with structured and organized information about entities, topics, and their relationships. It contains billions of facts about people, places, and things and enables users to search for Entities that Google knows about.
Introduced in 2012, the Knowledge Graph aims to provide more relevant, accurate, and useful search results to users by understanding the context and meaning of their queries, rather than just matching keywords.
It operates by collecting and analyzing information from a variety of sources, such as websites, databases, and other search engines, and transforming it into a massive database of interconnected entities and their attributes.
These entities can be anything from people, places, and things, to ideas, concepts, and events. And each is represented by a unique identifier, known as a Knowledge Graph ID, which can be used to link different types of information together.
Understanding Google Knowledge Graphs
The Knowledge Graph is designed to provide users with instant answers to their queries, displayed in a visually rich and interactive format known as a Knowledge Card. These cards typically include a summary of the entity’s key attributes, such as its name, description, images, videos, and related entities. They may also include additional information, such as reviews, ratings, and links to external sources.
When it comes to benefits for both users and businesses, the Knowledge Graph can significantly improve the user experience by providing more relevant search results.
For users, it provides more accurate and relevant search results, reduces the need for additional searches, and enhances the overall search experience. For businesses, it provides new opportunities for exposure and visibility, as well as the ability to control and manage their entity information in the Knowledge Graph.
Since the Knowledge Graph uses standard schema.org types, it also poses some challenges and limitations.
While schema.org provides a standardized set of types and properties for structured data, the challenge of integrating unstructured data into the Knowledge Graph remains.
Unstructured data sources, such as social media and user-generated content, are often difficult to integrate into the Knowledge Graph because they lack clear structure and organization. These data sources can contain a wide variety of information that may not easily fit into existing schema.org types.
As a result, it can be challenging to extract relevant entities and attributes from these data sources and map them onto the Knowledge Graph.
Fortunately, there are several techniques available to help organizations effectively manage their Knowledge Graphs and maximize the benefits they can enjoy. These include techniques such as entity extraction, entity resolution, and entity linking.
Entity extraction involves identifying and extracting relevant entities from unstructured data sources, such as named entities in text.
Entity resolution involves matching extracted entities to entities already present in the Knowledge Graph, reducing duplicate entries, and improving accuracy.
Entity linking involves linking extracted entities to relevant entities in the Knowledge Graph, improving the overall quality and completeness of the graph.
In conclusion, the Google Knowledge Graph represents a significant step forward in the evolution of search technology, and has the potential to transform the way we search for and discover information online.